Trinamic drivers
Stepper motors in a 3D printer are controlled by a variety of driver chips such as the common A4988 and DRV8825. These provide signals to the stepper motors to control the magnets and move them by micro-steps. Typically the motor is divided into 3200 steps per revolution, with 80 steps per millimeter of motion. At the movement rates of 3D printers, and due to the ringing produced by stepper motors, the vibrations from these steps can be very loud to the human ear.
Trinamic stepper drivers control stepper motors with greater finesse and interpolate the micro-steps to produce extremely quiet motion. Through SPI or serial control, you can change how the drivers manage motor current as well as the manner of current delivery. These drivers can even detect when a motor hits an obstruction, so they can act as endstops for simplified wiring. You can also set the driver current with Marlin G-code commands, removing the need to adjust physical trimpots.
Supported TMC drivers and features
| Driver | Control | StealthChop | Sensorless homing/probing | Driver monitoring | Hybrid threshold | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMC2100 | none | yes | no | no | no | Standalone mode only |
| TMC2130 | SPI | yes | yes | yes | yes | |
| TMC2160 | SPI | yes | yes | yes | yes | |
| TMC5130 | SPI | yes | yes | yes | yes | |
| TMC5160 | SPI | yes | yes | yes | yes | |
| TMC2208 TMC2225 | UART | yes | no | yes | yes | UART RX line requires an interrupt capable pin. Software UART isn’t supported on all platforms, such as DUE based boards. |
| TMC2209 TMC2226 | UART | yes | yes | yes | yes | |
| TMC2660 | SPI | no | not implemented | yes | no |
All configurable Trinamic stepper drivers can also be operated in standalone mode if they are pre-configured in hardware, either by hard connections or jumpers.
Installing the library
The TMC stepper drivers require an external library that allows Marlin to communicate with each driver.
For PlatformIO
PlatformIO will automatically download all libraries it requires, so skip directly to Wiring below.
Installing from Arduino IDE library manager
- Open up the Arduino IDE
- Go to Sketch -> Include Library -> Manage Libraries…
- Marlin 1.1.9 and up:
- Search for TMCStepper
- Older versions of Marlin
- Search for TMC2130Stepper or TMC2208Stepper
- Click
Install
Installing from a zip file
- Marlin 1.1.9 and up:
- Go to TMC library homepage
- Older versions of Marlin
- Go to the TMC2130 library page
- Go to the TMC2208 library page
- Click Clone or download -> Download ZIP
- In Arduino IDE and go to Sketch -> Include Library -> Add .ZIP Library…
- Navigate to the downloaded file and click the Open button.
Wiring
TMC drivers (except in standalone mode) require some extra wiring (Serial or SPI) to communicate with and configure the drivers. Boards like the SKR from BigTreeTech actually integrate this wiring directly into the motherboard.
SPI Control
The SPI bus requires 4 wires for communication. The SCK, MOSI, and MISO wires can be shared across all the drivers, while CK must be wired to a separate pin for each driver. These pins are labeled differently on the motherboard versus the driver:
| Motherboard | Driver |
|---|---|
| SCK | SCK |
| MOSI | SDI |
| MISO | SDO |
| CS | CS |
Software SPI
You can use pins other than the HW SPI pins by enabling TMC_USE_SW_SPI and defining the required pins:
TMC_SW_MOSI
TMC_SW_MISO
TMC_SW_SCK
UART (Serial) CONTROL
A 1K resistor is required between TX and PD_UART.
| Motherboard | Driver | |
|---|---|---|
| RX | PD_UART | |
| TX | (1kohm) | PD_UART |
The serial port on master is selected in the pins file for your board. Alternatively you can use the slower software serial by not selecting any of the hardware serial ports. Typically one port per one driver is needed.
Software UART
You can use free pins for UART by disabling all of the hardware serial options in your board’s pins file and by defining the _SERIAL_TX_PIN and _SERIAL_RX_PIN pins.
Note: The receive (RX) pins must be interrupt-capable pins. Transmit (TX) pins don’t have this limitation.
FYSETC drivers
As of this writing, we recommend getting the original Watterott drivers or the revised FYSETC v1.1 drivers to avoid additional headaches.
The FYSETC v1.0 drivers come pre-configured in standalone mode. So the drivers should work for moving the axes but you won’t be able to configure them or take advantage of their extra features. For full-featured drivers you’ll need to modify three solder bridges on the driver PCB.
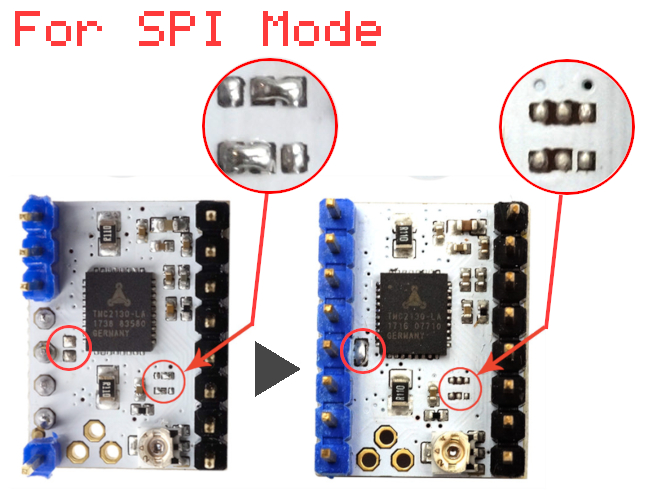
Some versions of the FYSETC v1.0 drivers come with a solder bridge left of the chip, some come with a bridging resistor. This connection needs to be opened for SPI connection to work. The two smaller bridges need to be configured as shown.
Features and configuration options
Several Trinamic-specific technologies are supported by Marlin.
- stealthChop is a technology that drives the motors using PWM voltage instead of current. The result is nearly inaudible stepping at low velocities. StealthChop has a lower stepping speed limit and if you need to move faster, for example travel moves, you may want to use spreadCycle or configure Hybrid Mode.
- spreadCycle is an alternative stepping mode. The driver will use four stages to drive the desired current into the stepper motor. SpreadCycle provides greater torque which might be useful if you’re experiencing skipped steps. The downside is slightly higher noise levels.
- stallGuard measures the load that is applied to the motor. If the load is sufficiently high, Marlin can react to the event. Such an event can be when we drive an axis to its physical limit and the signal provided by the driver can be detected just like an endstop. That way you can use the driver itself as an axis sensor negating the need to an additional endstop and the wiring needed. StallGuard is only active when the driver is in spreadCycle mode.
- Hybrid Mode: Marlin can configure the driver to automatically change between stepping modes using a user configured switching velocity. If the velocity is lower than the threshold the stepper is in quiet stealthChop mode. When the axis velocity increases the driver will automatically switch to spreadCycle.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| R_SENSE | The current sense resistor used in your product. * Watterott SilentStepSticks typically use 0.11ohm values. * Ultimachine Archim2 board has 0.22ohms. * Panucatt TMC2660 BigFoot drivers use 0.1ohms. |
| HOLD_MULTIPLIER | After the stepper hasn’t been moving for a short while, the driver can decrease the current and let the driver cool down. The multiplier is expressed as a decimal value in the range of 0.0 to 1.0. |
| INTERPOLATE | TMC drivers can take lower microstepping inputs, like the typical 16 and interpolate that to 256 microsteps which provides smoother movement. |
| CURRENT | Driver current expressed in milliamps. Higher current values will need active cooling and a heatsink. Low current values may warrant lower acceleration values to prevent skipping steps. |
| MICROSTEPS | Configures the driver to divide a full step into smaller microsteps which provide smoother movement. |
| SOFTWARE_DRIVER_ENABLE | Some drivers do not have a dedicated enable (EN) line and require the same function to be handled through software commands. |
| STEALTHCHOP | Default state for stepping mode on supporting TMC drivers. |
| CHOPPER_TIMING | Fine tune the spreadCycle chopper timings to optimize noise performance. A set of presets has been provided according to used driver voltage level, but a customized set can be used by specifying { <off_time[1..15]>, <hysteresis_end[-3..12]>, hysteresis_start[1..8] } |
| MONITOR_DRIVER_STATUS | Periodically poll the drivers to determine their status. Marlin can automatically reduce the driver current if the driver report overtemperature prewarn condition. The firmware can also react to error states like short to ground or open load conditions. |
| CURRENT_STEP | Reduce current value when Marlin sees OTPW error. |
| REPORT_CURRENT_CHANGE | Report to the user when automatically changing current setting. |
| STOP_ON_ERROR | If Marlin detects an error where the driver has shut down to protect itself, it can stop the print to save both time and material. |
| HYBRID_THRESHOLD | Configure the axis speed when the driver should switch between stealthChop and spreadCycle modes. |
| SENSORLESS_HOMING | Use the TMC drivers that support this feature to act as endstops by using stallGuard to detect a physical limit. |
| SENSORLESS_PROBING | Use stallGuard on supporting TMC drivers to replace a bed probe. Recommended to be used on delta printers only. |
| HOMING_SENSITIVITY | The Sensorless Homing sensitivity can be tuned to suit the specific machine. A higher value will make homing less sensitive. A lower value will make homing more sensitive. |
| TMC_DEBUG | Extend the information M122 reports. This will give you a lot of additional information about the status of your TMC drivers. |
| TMC_ADV | You can use this to add your own configuration settings. The requirement is that the command used must be part of the respective TMC stepper library. Remember to add a backslash () after each command! |
| AUTOMATIC_CURRENT_CONTROL | Replaced by MONITOR_DRIVER_STATUS.Marlin will poll the driver twice a second to see if the driver is in an error state. Such an error can be overtemperature pre-warn condition (OTPW) or short to ground or open load. Marlin can react to the temperature warning and automatically reduce the driver current. Short to ground error will disable the driver and Marlin can terminate the print to save time and material. |
G-codes
| Command | Configuration required | Description |
|---|---|---|
M122 | none | Test driver communication line and get debugging information of your drivers. TMC_DEBUG adds more reported information. |
M569 | TMC2130 or TMC2208 | Toggle between stealthChop and spreadCycle on supporting drivers. |
M906 | none | Set the driver current using axis letters X/Y/Z/E. |
M911 | MONITOR_DRIVER_STATUS | Report TMC prewarn triggered flags held by the library. |
M912 | MONITOR_DRIVER_STATUS | Clear TMC prewarn triggered flags. |
M913 | HYBRID_THRESHOLD | Set HYBRID_THRESHOLD speed. |
M914 | SENSORLESS_HOMING | Set SENSORLESS_HOMING sensitivity. |
M915 | TMC_Z_CALIBRATION | (Deprecated in Marlin 2.0.) Level your X axis by trying to move the Z axis past its physical limit. The movement is done at a reduced motor current to prevent breaking parts and promote skipped steps. Marlin will then rehome Z axis and restore normal current setting. |
Troubleshooting
- Some SilentStepSticks with variable 3-5V logic voltage (VIO) might get damaged if only powered over USB.
- Test driver communication status with
M122. - Test Marlin’s bugfix branch (on GitHub) to see if your issue is fixed.
- Test the latest TMCStepper library to see if your issue is fixed.
- Check all wiring and wire crimps.
- SPI: Use a multimeter to check connectivity all the way down the chain on all the communication lines.
- SPI conflict with the SD card? Solutions vary.
- UART:
- Make sure your receive (RX) pin is interrupt capable
- Check the resistance value between receive (RX) and transmit (TX) lines. You should see 1kOhm.
- Check connectivity from RX to the TMC chip
- Check 12V (24V) power in the Vm pin and 5V (3.3V) in the Vio pin.
- Check that configured pins match your firmware configuration.
- Enable
TMC_DEBUGand sendM122to see further debugging output.- Reported register values of either
0x00000000or0xFFFFFFFFare bad responses.
- Reported register values of either
- Try the examples provided by the respective library. Please detach any belts beforehand however, as the examples will not respect any endstop signals or physical limits. You may need to change the pin definitions.
- If you’re experiencing skipped steps there are a few things you can try
- First check for mechanical obstructions and that the parts move freely and do not bind
- Check that your nozzle doesn’t bump into your print if it starts curling upwards (cooling issue)
- Lower acceleration and jerk values
- Increase driver cooling
- Increase motor current
- Disable
INTERPOLATE
External resources
- Arduino library for TMC drivers (Replaces the following two)
-
For older Marlin you may need TMC2130 Arduino library or TMC2208 Arduino library
- SilentStepStick TMC2130 schematic and pinout
- Trinamic
- Watterott documentation
- stallGuard
- stealthChop
- spreadCycle
- Video guide by Thomas Sanladerer
- TMC2208 Torque testing by Alex Kenis